Baker Island
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Geography of Oceania (Australasia)
Baker Island is an uninhabited atoll located just north of the equator in the central Pacific Ocean at , about 3,100 km (1,675 nautical miles) southwest of Honolulu. Sometimes grouped together as part of the United States Minor Outlying Islands, it is about one-half of the way from Hawaii to Australia.
Baker Island National Wildlife Refuge consists of the 405 acre (1.64 km²) island and a surrounding 30,504 acres (123.45 km²) of submerged land. The island is now a National Wildlife Refuge managed by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as an insular area under the U.S. Department of the Interior. Baker Island is an unincorporated and unorganized territory of the U.S..
Its defense is the responsibility of the United States; though uninhabited, it is visited annually by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
History
The United States took possession of the island in 1857, claimed under the Guano Islands Act of 1856. It became a British Overseas Territory from 1886 to 1934. Its guano deposits were mined by U.S. and British companies during the second half of the 19th century. In 1935, a short-lived attempt at colonization was begun, as well as on nearby Howland Island. The settlement Meyerton had a population of four American civilians evacuated in 1942 after Japanese air and naval attacks. During World War II it was occupied by the U.S. military.
Since the war, Baker has been uninhabited. Feral cats were eradicated from the island in 1964. Public entry is by special-use permit from U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service only and generally restricted to scientists and educators.
Geography
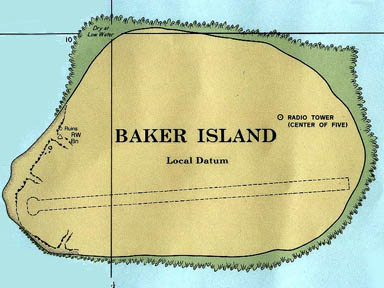
Located in the North Pacific Ocean at , the island is tiny at just 1.64 km² (405 acres) and 4.8 km of coastline. The climate is equatorial, with little rainfall, constant wind, and a strong sunshine. The terrain is low-lying and sandy: a coral island surrounded by a narrow fringing reef with a depressed central area. The highest point is 8 meters above sea level.
There are no natural fresh water resources. The island is treeless, with sparse vegetation consisting of grasses, prostrate vines, low growing shrubs, and some scattered ruins. A cemetery and remnants of structures from early settlement are located near the middle of the west coast. The island is primarily a nesting, roosting, and foraging habitat for seabirds, shorebirds, and marine wildlife.
The U.S. claims an exclusive economic zone of 200 nautical miles (370 km) and territorial sea of 12 nautical miles (22 km).
The island's Time zone: UTC-12
Transportation
There are no ports or harbors, with anchorage available only offshore. There is one boat landing area along the middle of the west coast. There is an abandoned World War II runway, 1,665 meters long, which is completely covered with vegetation and unusable.
Natural hazards: The narrow fringing reef surrounding the island can be a maritime hazard and there is a day beacon near the middle of the west coast.
Similarly Named Islands
- Baker's Island, Mass.
- Baker Island - Acadia Nat. Park, Maine